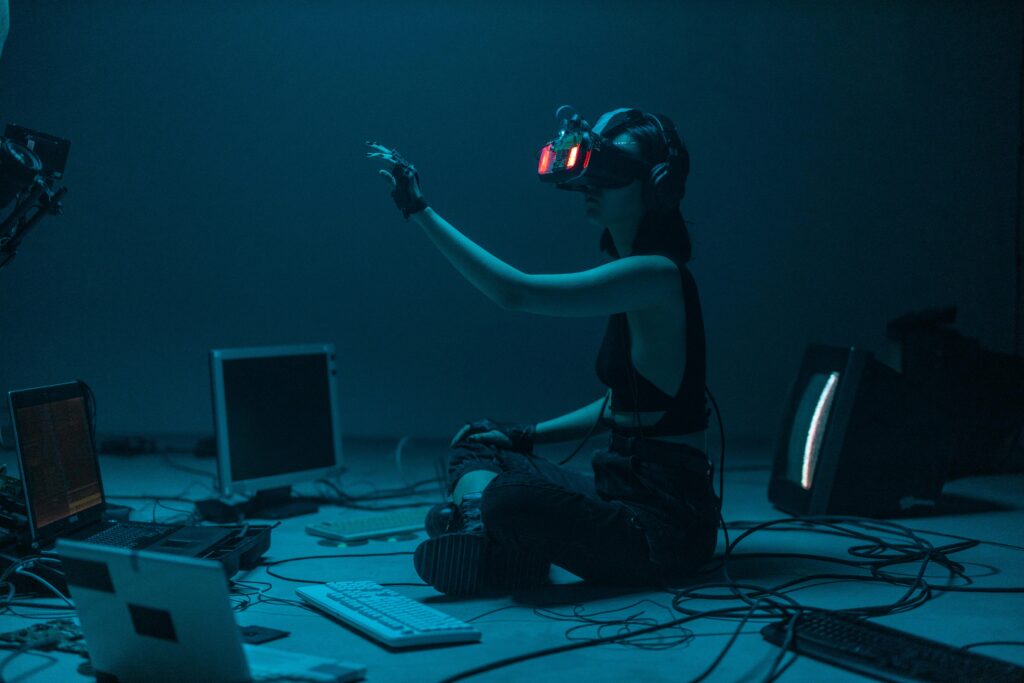
Imagine walking into your office and being greeted not just by colleagues, but by a digital assistant that already knows your schedule, has prioritized your emails, and even suggested improvements to your presentation—all before you’ve had your first sip of coffee. This isn’t science fiction. It’s happening right now, thanks to artificial intelligence (AI) reshaping the modern workplace.
AI is no longer a futuristic concept reserved for tech giants and sci-fi movies. From small startups to multinational corporations, businesses across industries are integrating AI into daily operations. Whether it’s automating repetitive tasks, enhancing decision-making, or improving customer service, AI is transforming how we work—fast. But with great power comes great responsibility. As AI becomes more embedded in our professional lives, it brings both exciting opportunities and complex challenges.
In this article, we’ll explore how AI is revolutionizing the workplace, from boosting productivity to redefining job roles. We’ll dive into real-world examples, discuss the ethical dilemmas, and offer practical tips for professionals and organizations navigating this new era. Whether you’re a manager, an employee, or simply curious about the future of work, understanding AI’s role is no longer optional—it’s essential. Let’s uncover what AI means for your career, your company, and the future of work as we know it.
1. The Rise of AI in Everyday Work Life
AI isn’t just for Silicon Valley engineers or data scientists anymore. It’s quietly becoming part of our daily work routines—often without us even noticing. Think about the last time you used a grammar-checking tool like Grammarly, received meeting suggestions from your calendar app, or got a customer service reply from a chatbot. These are all powered by AI.
According to a 2023 report by McKinsey, 50% of companies have adopted AI in at least one business function. That’s up from just 20% in 2017. The most common uses? Automating internal processes, enhancing customer experience, and supporting data analysis. But what does this mean for the average worker?
Take Sarah, a marketing coordinator at a mid-sized firm. Her day used to be filled with manually sorting leads, scheduling social media posts, and analyzing campaign data. Now, AI tools automatically segment her audience, recommend optimal posting times, and generate performance reports. This doesn’t mean Sarah is obsolete—in fact, she’s more valuable than ever. With AI handling the routine, she can focus on creative strategy and building client relationships.
This shift is happening across industries. In healthcare, AI helps doctors analyze medical images faster. In finance, algorithms detect fraudulent transactions in real time. In manufacturing, smart systems predict equipment failures before they happen.
The key takeaway? AI isn’t replacing humans—it’s augmenting them. It’s like having a super-smart assistant that never sleeps, handles the boring stuff, and lets you focus on what you do best: thinking, creating, and connecting.
But as AI becomes more capable, questions arise: What jobs are safe? Who controls the data? And how do we ensure these systems are fair? These are exactly the challenges we’ll explore next.
2. Boosting Productivity: How AI Helps Teams Do More with Less
One of the biggest promises of AI in the workplace is increased productivity. And the numbers back it up. A study by Accenture found that AI could boost labor productivity by up to 40% by 2035. That’s not just a small efficiency gain—it’s a game-changer.
So how does it work? Let’s break it down.
AI excels at handling repetitive, time-consuming tasks. For example:
- Email sorting and prioritization (tools like Outlook’s Focused Inbox)
- Data entry and form filling (automated by robotic process automation, or RPA)
- Scheduling meetings (using AI assistants like Clara or x.ai)
- Generating reports (from raw data in seconds, not hours)
These may seem like small wins, but they add up. Consider this: the average employee spends 28% of their workweek managing emails. That’s nearly 11 hours a week—time that could be spent on strategic thinking, collaboration, or skill development.
AI also enhances decision-making. Instead of relying on gut feelings or incomplete data, managers can use AI-powered analytics to spot trends, forecast sales, or identify employee burnout risks. For instance, a retail company might use AI to analyze customer behavior and adjust inventory in real time, reducing waste and increasing sales.
Moreover, AI supports remote and hybrid teams. Virtual assistants can transcribe meetings, summarize action items, and even detect team sentiment through tone analysis. This helps keep everyone aligned—no matter where they’re logging in from.
But here’s the catch: AI only boosts productivity if it’s used wisely. Poorly implemented systems can create confusion, increase workload, or erode trust. That’s why successful AI adoption isn’t just about technology—it’s about people, processes, and purpose.
The goal isn’t to automate everything. It’s to automate the right things—freeing up human talent for higher-value work.
3. The Human Side of AI: Jobs, Skills, and the Future of Work
Now, let’s address the elephant in the room: Will AI take my job?
It’s a valid concern. Headlines often scream about robots replacing workers, and while some roles are at risk, the full picture is more nuanced.
The World Economic Forum estimates that by 2025, 85 million jobs may be displaced by AI and automation. But here’s the hopeful part: 97 million new roles could emerge at the same time. The future isn’t about fewer jobs—it’s about different jobs.
Think of it like the industrial revolution. When machines replaced manual labor, many feared mass unemployment. But over time, new industries and professions emerged—mechanics, engineers, factory supervisors. The same is happening today.
AI is creating demand for roles like:
- AI trainers (teaching models to understand human language)
- Ethics officers (ensuring AI systems are fair and transparent)
- Data annotators (labeling information for machine learning)
- Hybrid roles (e.g., “marketing analyst + AI specialist”)
Even in traditional jobs, AI is changing skill requirements. A salesperson today needs to understand CRM analytics. A nurse might use AI diagnostics. A teacher could personalize lessons using adaptive learning platforms.
So, what should you do? Focus on future-proof skills:
- Critical thinking (AI gives answers, but humans ask the right questions)
- Emotional intelligence (machines can’t empathize or build trust)
- Creativity (AI generates ideas, but humans judge and refine them)
- Adaptability (the ability to learn and relearn is more valuable than ever)
Upskilling isn’t just for individuals—companies must invest in training too. Google’s “Grow with Google” initiative, for example, offers free AI and digital skills courses to employees and the public. Microsoft and Amazon have similar programs.
The message is clear: AI won’t replace you, but someone using AI might. The best defense is continuous learning.
4. Ethical Challenges: Bias, Privacy, and Trust in AI Systems
While AI offers incredible benefits, it’s not without risks. One of the biggest concerns? Bias in AI decision-making.
Here’s a real-world example: In 2018, Amazon scrapped an AI recruiting tool because it was discriminating against women. Why? The system was trained on resumes submitted over 10 years—most of which came from men. As a result, it learned to downgrade resumes with words like “women’s chess club” or degrees from all-female colleges.
This isn’t an isolated case. AI systems can inherit human biases from the data they’re trained on. Whether it’s in hiring, loan approvals, or performance reviews, biased AI can lead to unfair outcomes—especially for marginalized groups.
Then there’s privacy. AI thrives on data, but where does that data come from? Employee monitoring tools, for instance, can track keystrokes, mouse movements, and even webcam activity. While companies argue this improves productivity, employees may feel surveilled and stressed.
A 2022 Gartner survey found that 60% of employees are uncomfortable with AI monitoring their work. That’s a trust issue—one that can damage morale and culture.
And what about transparency? Many AI systems are “black boxes”—we see the input and output, but not how decisions are made. If an AI denies someone a promotion, how do we explain why?
So, what can organizations do?
- Audit AI systems regularly for bias and fairness
- Use diverse training data to avoid skewed outcomes
- Be transparent about how AI is used and what data is collected
- Give employees a voice in AI decisions that affect them
Ethical AI isn’t just the right thing to do—it’s good for business. Companies that prioritize fairness and trust are more likely to retain talent, avoid lawsuits, and build strong reputations.
5. AI and Collaboration: Enhancing Teamwork, Not Replacing It
Here’s a surprising truth: AI can make us more human at work.
At first glance, that might sound contradictory. After all, AI is digital, logical, and emotionless. But when used thoughtfully, it can actually enhance human connection.
How? By removing friction from collaboration.
Imagine a global team spread across five time zones. Coordinating meetings, sharing files, and tracking progress can be a nightmare. AI-powered tools like Slack’s workflow builder, Notion’s AI assistant, or Microsoft Teams’ Copilot can streamline communication, suggest agenda items, and even summarize long threads.
AI can also break down language barriers. Tools like Google Translate or DeepL allow teams to collaborate in real time, regardless of native language. Some platforms now offer live translation in video calls—making inclusivity easier than ever.
But AI doesn’t just connect people—it can help understand them better.
Sentiment analysis tools can scan team messages or feedback surveys to detect stress, disengagement, or conflict. A manager might receive an alert: “Team morale dropped after the last project deadline.” This allows for proactive support—like adjusting workloads or organizing a team check-in.
And let’s not forget creativity. AI can spark new ideas during brainstorming sessions. For example, a design team might use AI to generate logo concepts, which they then refine together. The AI provides inspiration; the humans provide judgment and emotion.
The lesson? AI isn’t here to replace teamwork—it’s here to supercharge it. The most successful teams of the future won’t be human vs. machine, but human + machine working in sync.
6. Practical Tips for Embracing AI at Work
You don’t need to be a tech expert to benefit from AI. Here are five simple, actionable steps anyone can take—today.
- Start Small
Don’t try to overhaul your entire workflow. Pick one repetitive task—like scheduling meetings or organizing files—and find an AI tool to help. Try Calendly for scheduling or Trello with Butler for task automation. - Learn the Basics
You don’t need to code, but understanding AI fundamentals helps. Platforms like Coursera, edX, or LinkedIn Learning offer beginner-friendly courses on AI and digital literacy. - Ask Questions
If your company uses AI tools, ask how they work. What data do they use? Who oversees them? Being curious shows initiative and helps build trust. - Use AI to Learn
Tools like Khanmigo (from Khan Academy) or ChatGPT can act as personal tutors. Ask them to explain concepts, quiz you, or help draft emails. - Stay Human
Remember: AI is a tool, not a replacement. Focus on what makes you uniquely human—empathy, creativity, and judgment. Use AI to enhance those strengths, not replace them.
Bonus tip for leaders: Create a “test and learn” culture. Encourage teams to experiment with AI tools, share results, and iterate. Celebrate both successes and failures—innovation requires risk.
7. The Bigger Picture: AI as a Force for Positive Change
Beyond efficiency and productivity, AI has the potential to drive meaningful social impact in the workplace.
Consider accessibility. AI-powered tools like speech-to-text, screen readers, and voice-controlled interfaces are making work environments more inclusive for people with disabilities. Microsoft’s Seeing AI app, for example, describes the world for visually impaired users—helping them navigate offices, read documents, and participate in meetings.
AI is also supporting mental health. Apps like Woebot or Wysa use AI to provide cognitive behavioral therapy techniques, helping employees manage stress and anxiety. Some companies are integrating these tools into their wellness programs.
And let’s talk about sustainability. AI can optimize energy use in offices, reduce waste in supply chains, and support remote work—cutting carbon emissions. Google, for instance, uses AI to reduce energy consumption in its data centers by up to 40%.
When guided by ethics and empathy, AI becomes more than a business tool—it becomes a force for good.
But this future isn’t automatic. It requires intentional choices: Who builds the AI? Who benefits from it? And who holds it accountable?
As we shape the future of work, let’s ensure it’s not just smarter—but fairer, kinder, and more human.
Conclusion: Embracing the AI-Powered Workplace with Confidence
AI is no longer a distant possibility—it’s here, reshaping how we work, collaborate, and grow. From automating mundane tasks to unlocking new levels of creativity, the opportunities are vast. But so are the challenges: ethical dilemmas, job transitions, and the need for lifelong learning.
The key takeaway? AI isn’t about replacing humans—it’s about redefining what’s possible. The most successful professionals and organizations won’t be those who resist AI, but those who learn to work with it.
Start by embracing small changes. Use an AI tool to save time. Take a course to build your digital confidence. Ask thoughtful questions about how AI is used in your workplace.
And remember: technology evolves fast, but human values—empathy, integrity, creativity—endure. These are your superpowers in the age of AI.
So, what’s your next step? Will you let AI work for you, or will you work with AI to build a better future?
We’d love to hear your thoughts. Have you used AI at work? What surprised you? What worries you? Share your experience in the comments below—let’s learn from each other as we navigate this exciting new era together.

Danilo Ferreira is a passionate entrepreneur, travel, and financial freedom enthusiast, always seeking new ways to expand his horizons and live with purpose. Driven by a high-performance mindset, he combines discipline and curiosity to achieve ambitious goals, exploring the world while building projects that reflect his vision of independence and continuous growth.